
The homologous chromosomes will pair off and be connected by protein scaffolds, at which point genetic recombination (crossing-over) can occur. Meiosis begins with Prophase I, in which the chromosomes condense into more manageable sizes and densities, and the nuclear membrane dissolves. Meiosis can be divided into two main sections-Meiosis I and Meiosis II-as there are two cellular division events that take place. Each of these sections include four smaller stages, prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase, which are also present during mitotic divisions. At this point, once all the chromosomes have been replicated, meiosis can begin! Stages of Meiosis These replicas are bound by a centromere and are referred to as sister chromatids. The sole purpose of meiosis is to produce the gametes-eggs and sperm- and have each of them contain exactly half the number of chromosomes of the original germ line cell.Įxplaining the entire cellular life cycle goes beyond the scope of this article, but prior to the start of meiosis, during the S phase of interphase, all of the DNA in the germ line cells is replicated, such that each cell contains two copies of identical genetic material. Haploid, on the other hand, refers to cells that contain only one set of chromosomes. Diploid means possessing two sets of chromosomes, one from the male and one from the female. These germ line cells in a diploid organism, like a human, are diploid in nature.
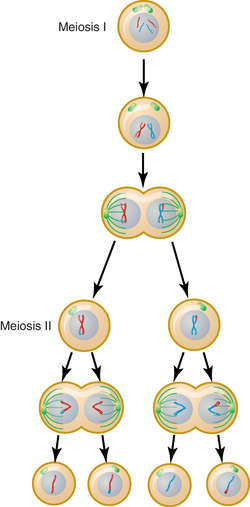
Meiosis is only applicable for sex cells, namely the germ line cells that can be found in male testes and the female ovary. Meiosis is different from mitosis, in that 4 haploid cells are the end result, whereas the end result in mitosis is 2 diploid cells. More specifically, meiosis can be found in all sexually reproducing animals, plants and fungi, whether they are single-celled or multicellular eukaryotes. For simplicity sake, we will be looking at meiosis from a primarily human perspective, although it occurs in all animals and plants within their respective sex cells and organs. The second form of cellular division, meiosis, is much more specialized and specifically located, namely in the reproductive cells of an organism. Mitosis is the method used by somatic cells, which make up the vast majority of our bodies, and are responsible for cellular division in tissues, organs, veins etc. There are two forms of cellular division in the body.
PROPHASE 2 DEFINITION SKIN
In humans, this is not applicable to all cells, such as neurons, skin cells, heart cells and fat cells, but for the more than 200 other types of cells in the body, cellular division is their fundamental purpose-passing on genetic material, an instruction manual, per se, to healthy new cells. One of the most impressive things about living organisms, and human beings specifically, is the ability to perpetually regrow our cells through the process of cell division.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
